Exploring the differences between Functional Medicine and Traditional Healthcare, this article provides a detailed comparison that sheds light on the unique aspects of each approach. From personalized care to treatment modalities, delve into the world of healthcare practices with a fresh perspective.
As we unravel the core principles and methodologies of Functional Medicine and Traditional Healthcare, you'll gain insights into how these two systems diverge in their approach towards patient care and overall well-being.
Functional Medicine
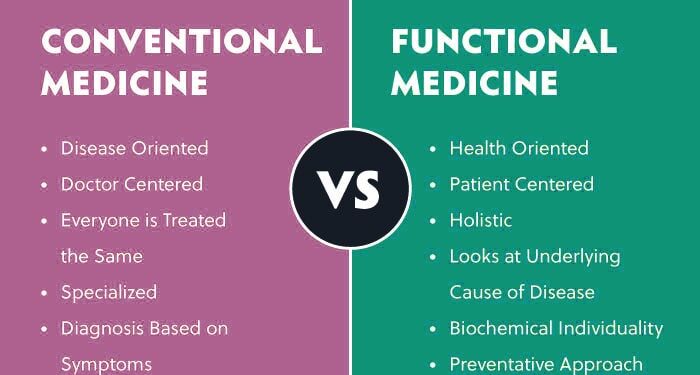
Functional medicine is a patient-centered approach that focuses on addressing the root cause of illness rather than just treating symptoms. This holistic approach considers the unique genetic makeup, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices of each individual to create personalized treatment plans.
Core Principles of Functional Medicine
- Understanding the patient as a whole person, not just a set of symptoms
- Identifying and addressing the underlying causes of disease
- Emphasizing prevention through nutrition, diet, and lifestyle modifications
- Using a collaborative approach between patient and practitioner
Conditions Addressed by Functional Medicine
- Chronic conditions such as autoimmune diseases, diabetes, and heart disease
- Gastrointestinal disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and Crohn's disease
- Hormonal imbalances, including thyroid issues and adrenal fatigue
Personalized Approach of Functional Medicine
Functional medicine practitioners take the time to listen to patients' concerns, conduct in-depth evaluations, and use advanced testing to uncover the root cause of their symptoms. Treatment plans are tailored to each individual's unique needs, focusing on lifestyle changes, nutrition, supplements, and mind-body practices.
Role of Nutrition and Lifestyle in Functional Medicine
Nutrition and lifestyle choices play a crucial role in functional medicine, as they can either promote health or contribute to the development of chronic diseases. Practitioners work with patients to optimize their diets, incorporate exercise routines, manage stress, and improve sleep patterns to support overall well-being and long-term health.
Traditional Healthcare
In traditional healthcare systems, the typical approach involves treating symptoms and diseases using standardized protocols and guidelines.
Common Treatments and Medications
Common treatments in traditional healthcare include prescription medications, surgeries, and other invasive procedures. Medications such as antibiotics, painkillers, and antihypertensives are frequently prescribed.
Contrast with Functional Medicine
Traditional healthcare tends to have a disease-centered approach, focusing on treating the specific ailment or condition. In contrast, functional medicine takes a patient-centered approach, looking at the individual as a whole and addressing the root cause of health issues.
Role of Preventive Care
In traditional healthcare, preventive care often involves routine screenings, vaccinations, and health education programs. The goal is to detect and prevent diseases before they become serious or life-threatening.
Patient-Centered Care
Functional medicine puts a strong emphasis on patient-centered care, prioritizing individual patient needs and goals above all else. This approach focuses on treating the whole person, taking into account their unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors to create personalized treatment plans.Traditional healthcare, on the other hand, may sometimes overlook personalized care due to time constraints, standardized treatment protocols, and a focus on symptom management rather than addressing the root cause of the health issue.
Patients often feel like just another number in the system, with limited opportunities to discuss their concerns and preferences.The impact of patient-centered care on treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction is significant. When patients feel heard, understood, and actively involved in their healthcare journey, they are more likely to adhere to treatment plans, experience better outcomes, and report higher levels of satisfaction with their care.
Patient-Centered Care Comparison
| Aspect | Functional Medicine | Traditional Healthcare |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Focuses on individual patient needs and goals | Often follows standardized protocols |
| Treatment Plans | Personalized based on genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors | May rely more on symptom management |
| Communication | Encourages open dialogue and active patient involvement | Limited time for patient consultations |
| Outcomes | Improved treatment adherence and patient satisfaction | Varied outcomes depending on patient-doctor relationship |
Integrative Approaches
Functional medicine takes an integrative approach by combining various healthcare modalities to address the root causes of illness and promote overall well-being. This approach considers the interconnectedness of the body systems and aims to treat the whole person rather than just the symptoms.
Complementary Therapies in Functional Medicine
Functional medicine often incorporates complementary therapies such as acupuncture, chiropractic care, massage therapy, herbal medicine, nutritional counseling, and mind-body techniques like meditation and yoga. These therapies are used alongside conventional treatments to support the body's natural healing processes and optimize health outcomes.
Benefits of Integrating Different Approaches
Integrating different approaches in healthcare allows for a more personalized and holistic treatment plan tailored to the individual needs of each patient. By combining conventional medicine with complementary therapies, patients may experience improved outcomes, reduced side effects, and better overall health and well-being.
Acupuncture
Helps to restore the flow of energy in the body and alleviate pain.
Chiropractic care
Focuses on spinal alignment and nervous system function for overall health.
Massage therapy
Promotes relaxation, reduces muscle tension, and enhances circulation.
Herbal medicine
Uses plant-based remedies to support the body's healing processes.
Nutritional counseling
Provides guidance on healthy eating habits and lifestyle changes for optimal health.
Mind-body techniques
Such as meditation and yoga, help reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the debate between Functional Medicine and Traditional Healthcare offers a rich tapestry of contrasting ideologies. By understanding the nuances of each approach, individuals can make informed decisions about their healthcare journey, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and quality of life.
FAQ Summary
How does Functional Medicine differ from Traditional Healthcare?
Functional Medicine focuses on addressing the root cause of illnesses by considering the individual's unique genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Traditional Healthcare, on the other hand, typically treats symptoms rather than underlying causes.
What role does nutrition play in Functional Medicine?
Nutrition is a cornerstone of Functional Medicine, emphasizing the importance of a personalized diet tailored to each individual's specific health needs. This approach aims to optimize health outcomes by addressing nutritional deficiencies and promoting overall wellness.
How does patient-centered care impact treatment outcomes?
Patient-centered care, as practiced in Functional Medicine, leads to improved treatment outcomes and higher patient satisfaction levels. By prioritizing individual needs and goals, healthcare providers can offer tailored solutions that resonate with patients on a personal level.