Embark on a journey exploring the intricate relationship between gut health and brain function. Delving into the world of gut microbiota, diet impact, and inflammation, this discussion sheds light on how our gut influences our cognitive well-being.
As we uncover the role of probiotics and prebiotics, discover how these elements play a crucial part in maintaining a healthy gut-brain axis.
Gut Microbiota
The gut microbiota, comprised of trillions of microorganisms living in the digestive tract, plays a crucial role in maintaining gut health and overall well-being. These microbes include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other organisms that contribute to various functions within the body.
Beneficial Bacteria in the Gut and Their Functions
The gut is home to numerous beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, which help in digestion, absorption of nutrients, and the synthesis of vitamins like B and K. These bacteria also play a key role in maintaining a healthy balance in the gut microbiome and supporting the immune system.
- Lactobacillus: Known for its role in fermenting sugars and producing lactic acid, Lactobacillus helps maintain the acidic environment in the gut, which prevents the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Bifidobacterium: This type of bacteria aids in breaking down complex carbohydrates and promoting the growth of other beneficial microorganisms in the gut.
Influence of Gut Microbiota on Brain Function through the Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain, where the gut microbiota play a significant role. The microbiota can influence brain function and behavior through various pathways, including the production of neurotransmitters, immune modulation, and the regulation of inflammation.
- Production of Neurotransmitters: Gut bacteria can produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for mood regulation and cognitive function.
- Immune Modulation: The gut microbiota interact with the immune system, affecting inflammation levels that can impact brain health and cognitive processes.
- Regulation of Inflammation: Imbalances in the gut microbiota can lead to increased inflammation, which has been linked to neurological disorders like Alzheimer's and depression.
Diet and Gut Health
Diet plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut. The food we consume directly impacts the composition and diversity of our gut microbiota, which in turn affects our overall health.
Impact of Diet on Gut Health
Our diet significantly influences the health of our gut. A diet rich in fiber from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. On the other hand, a diet high in sugar and processed foods can lead to an imbalance in gut microbiota, potentially causing inflammation and other health issues.
High-Fiber Diet vs. High-Sugar Diet on Gut Microbiota Diversity
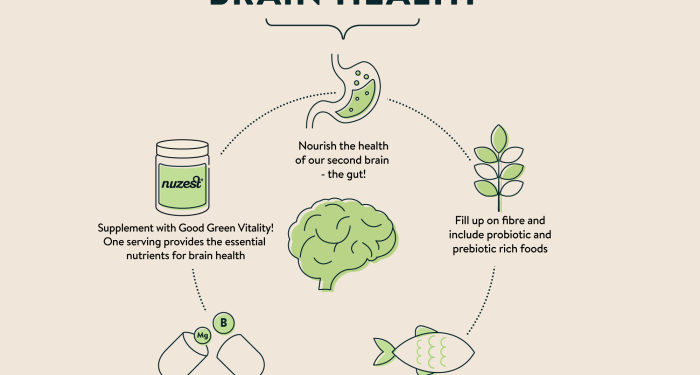
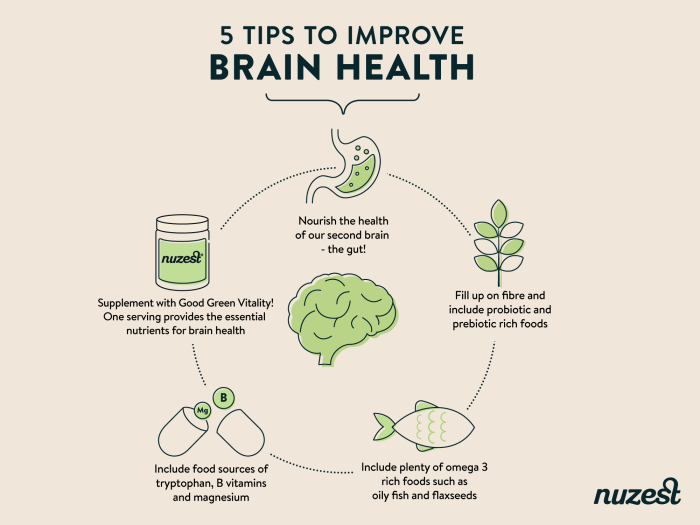
A high-fiber diet is beneficial for gut health as it provides nutrients for the good bacteria in the gut to thrive. Fiber helps in the production of short-chain fatty acids, which are essential for gut health. In contrast, a high-sugar diet can reduce microbial diversity in the gut and promote the growth of harmful bacteria, leading to gut dysbiosis.
Fermented Foods and Healthy Gut Microbiome
Fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain beneficial probiotics that can help improve gut health. These probiotics can enhance the diversity of gut microbiota and support a healthy gut microbiome. Incorporating fermented foods into your diet can contribute to better digestion and overall gut health.
Inflammation and Gut-Brain Connection
Understanding the relationship between inflammation, gut health, and brain function is crucial for overall well-being. Inflammation in the gut can have a direct impact on cognitive abilities and brain health.
Impact of Gut Inflammation on Cognitive Abilities
When the gut is inflamed, it can lead to a condition known as "leaky gut syndrome," where the intestinal barrier becomes compromised. This can allow harmful substances to pass through the gut lining and enter the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and inflammation throughout the body, including the brain.
This chronic inflammation can impair cognitive functions such as memory, focus, and mood regulation
Strategies to Reduce Gut Inflammation for Improved Brain Health
- Avoiding inflammatory foods: Processed foods, refined sugar, and artificial additives can contribute to gut inflammation. Opt for a diet rich in whole foods, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to reduce inflammation.
- Consuming anti-inflammatory foods: Incorporate foods like fatty fish, nuts, seeds, and leafy greens that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants to combat inflammation in the gut.
- Probiotics and prebiotics: Adding probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut, as well as prebiotic foods like bananas, onions, and garlic, can help restore balance to the gut microbiota and reduce inflammation.
- Managing stress: Chronic stress can exacerbate gut inflammation. Practicing mindfulness techniques, yoga, or meditation can help reduce stress levels and promote gut health.
- Regular exercise: Physical activity can help regulate inflammation in the body, including the gut. Aim for regular exercise to support overall gut and brain health.
Probiotics and Prebiotics
Probiotics and prebiotics play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut and supporting optimal brain function. While they both promote gut health, they differ in their functions and sources.
Probiotics
Probiotics are live bacteria and yeasts that are beneficial for your digestive system. They help maintain the balance of good bacteria in the gut, which is essential for proper digestion and absorption of nutrients. Probiotics also support the immune system and can help alleviate symptoms of digestive disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- Examples of foods rich in probiotics include yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kombucha.
- Benefits of probiotics include improved digestion, enhanced immune function, and potential reduction in inflammation throughout the body.
Prebiotics
Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. They help stimulate the growth and activity of these good bacteria, promoting a healthy gut microbiome. Prebiotics are essential for maintaining a diverse and balanced gut flora, which is crucial for overall health and well-being.
- Foods rich in prebiotics include garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, and whole grains.
- Benefits of prebiotics include improved gut health, enhanced nutrient absorption, and potential reduction in the risk of certain chronic diseases.
Summary
In conclusion, the connection between gut health and brain function is profound. By understanding and nurturing our gut microbiome, we pave the way for optimal cognitive function and overall well-being.
Query Resolution
How does gut microbiota influence brain function?
Gut microbiota produce neurotransmitters and communicate with the brain through the gut-brain axis, impacting cognitive processes.
What foods are rich in probiotics and prebiotics?
Probiotic-rich foods include yogurt and kimchi, while prebiotics can be found in bananas and onions, supporting gut health.
Can gut inflammation affect cognitive abilities?
Yes, conditions like leaky gut syndrome can lead to inflammation that affects the brain, impacting cognitive function.